Smart packaging refers to packaging solutions that incorporate advanced technologies to enhance functionality, improve user experience, and provide valuable data. This innovative approach to packaging integrates digital and sensory technologies to offer benefits beyond traditional packaging, such as tracking, authentication, and interactive features. Smart packaging is transforming various industries, including food and beverages, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and electronics.
Download White Paper: https://www.towardspackaging.com/personalized-scope/5055
What is Smart Packaging?
Smart packaging involves the use of technologies that allow packaging to interact with consumers, provide real-time information, and monitor product conditions. These technologies can include sensors, QR codes, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), NFC (Near Field Communication), and more. The primary goal is to enhance the functionality of packaging and improve the overall consumer experience.
Key Features of Smart Packaging
- Interactive Capabilities:
- Smart packaging can engage consumers through interactive features such as QR codes, NFC tags, and augmented reality (AR). These features provide additional information about the product, promotional content, or interactive experiences.
- Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring:
- Technologies like RFID and IoT (Internet of Things) enable real-time tracking of products throughout the supply chain. This helps in monitoring product conditions, managing inventory, and ensuring timely deliveries.
- Authentication and Anti-Counterfeiting:
- Smart packaging can help verify the authenticity of products using technologies like holograms, tamper-evident seals, and digital codes. This is particularly important for pharmaceuticals and high-value goods.
- Condition Monitoring:
- Packaging with embedded sensors can monitor environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure. This ensures that products are stored and transported under optimal conditions, especially for sensitive items like food and pharmaceuticals.
- Enhanced User Experience:
- Features like smart labels and interactive designs can provide consumers with personalized information, usage instructions, and product recommendations, enhancing their overall experience with the product.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us at sales@towardspackaging.com
Examples of Smart Packaging Technologies
- RFID and NFC Tags:
- RFID Tags: Used for tracking and managing inventory by providing real-time data on product location and movement.
- NFC Tags: Enable consumers to access product information or promotional content by simply tapping their smartphones against the packaging.
- QR Codes:
- QR codes can be scanned by smartphones to access product details, promotional offers, or interactive content. They are widely used for marketing and providing additional information.
- Temperature Sensors:
- Embedded in packaging to monitor and record temperature changes, ensuring that products like vaccines and perishable goods are stored within required conditions.
- Augmented Reality (AR):
- AR-enabled packaging allows consumers to interact with the product through their smartphones or tablets, providing immersive experiences and additional product information.
- Smart Labels:
- Labels that change color or provide visual indicators to show the freshness or quality of the product. They can also include embedded sensors for real-time data collection.
Benefits of Smart Packaging
- Improved Product Safety:
- By monitoring and controlling environmental conditions, smart packaging helps ensure that products are safe for consumption and use, reducing the risk of spoilage or degradation.
- Enhanced Consumer Engagement:
- Interactive features and personalized content create a more engaging experience for consumers, fostering brand loyalty and increasing customer satisfaction.
- Efficient Supply Chain Management:
- Real-time tracking and monitoring provide valuable insights into inventory levels, product movement, and potential issues, leading to more efficient supply chain operations.
- Counterfeit Prevention:
- Advanced authentication features help prevent counterfeit products from entering the market, protecting both consumers and brand integrity.
- Data Collection and Analytics:
- Smart packaging enables the collection of valuable data on consumer behavior, product usage, and supply chain performance, which can be used for strategic decision-making and marketing.
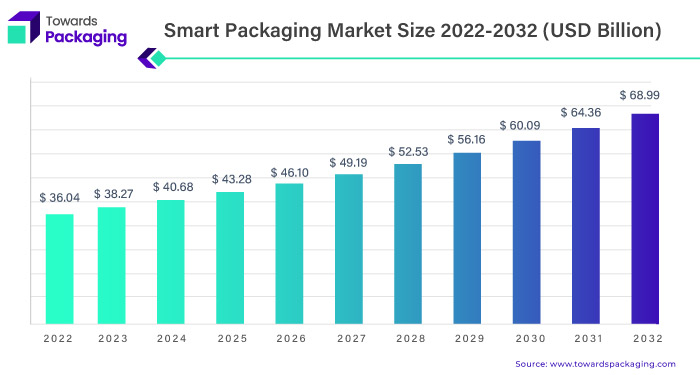
Smart Packaging Market Size, Share Analysis 2023-2032
The global smart packaging market size was estimated at USD 36.04 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach around USD 68.99 billion by 2032 with a registered CAGR of 6.8% from 2023 to 2032.
Get the latest insights on packaging industry segmentation with our Annual Membership – https://www.towardspackaging.com/get-an-annual-membership
Smart packaging entails strategically integrating advanced technologies, such as RFID tags, sensors, and QR codes, within product packaging to drive enhanced business outcomes. This innovative approach empowers manufacturers to actively monitor and trace their products across the complete supply chain, encompassing production, distribution, and end-consumer engagement. By infusing packaging solutions with heightened intelligence, smart packaging enables proactive thinking, seamless communication, and interactive capabilities with the packaged product and discerning consumers.
The adoption of smart packaging delivers a range of substantial advantages. Firstly, it elevates the customer experience by providing additional functionalities and features that optimize convenience, safety, and usability. Embedded sensors within the packaging facilitate real-time monitoring of vital parameters like humidity, temperature, and integrity, ensuring optimal product quality and integrity throughout the entire value chain.
Moreover, smart packaging bolsters product safety and security. Manufacturers can achieve robust product tracking, authentication, and anti-counterfeiting measures by leveraging advanced technologies like RFID tags and QR codes. This safeguards consumer well-being, protects brand reputation, and fosters trust within the marketplace.
Furthermore, smart packaging supports sustainability initiatives by optimizing inventory management, reducing waste, and enabling efficient recycling processes. By leveraging RFID tags, supply chain operations can be streamlined, minimizing excess inventory and mitigating environmental impact. QR codes provide consumers valuable information on proper disposal methods and recycling options, facilitating responsible post-consumption practices.
Ultimately, smart packaging catalyzes ensuring superior product quality, optimizing supply chain efficiency, and cultivating enduring customer relationships. By integrating advanced capabilities such as sensing, evaluation, identification, tracking, and reporting, smart packaging enables manufacturers to consistently meet rigorous quality standards while delivering a seamless and enriched customer experience.
Smart Packaging is experiencing robust and consistent growth, driven by its ability to adapt to the ever-changing and demanding market landscape. With the continuous advancement of smartphones, which enable enhanced advertising and authentication applications, consumer expectations are on the rise. They now seek packaging solutions that are more intelligent and interactive. Concurrently, significant investment and significant packaging companies invest substantial resources into smart packaging. However, it is essential to note that the regulatory environment is also becoming increasingly stringent, potentially imposing restrictions on promising emerging technologies.
The amalgamation of these factors, along with the evolving social demographic, highlights the challenges the smart packaging industry faces. Nevertheless, it also underscores the vast array of opportunities available across all active and intelligent packaging sectors, provided they remain receptive and adaptable to change.